Using Tailscale with your firewall
Most of the time, Tailscale should work with your firewall out of the box. Thanks to NAT traversal, nodes in your tailnet can connect directly peer to peer, even through firewalls. To get many firewalls working with Tailscale, try opening a firewall port to establish a direct connection.
For some firewalls, though, it is particularly difficult to establish a direct connection, so your traffic relies on DERP relay servers as a fallback, which may lead to slower connections. See below the list of known issues and workarounds for using Tailscale with your firewall provider.
Types of connections
Tailscale will either connect your nodes directly or via a DERP relay.
Tailscale tries to connect your nodes directly peer to peer, and does so nearly all of the time. Where this is not possible, Tailscale will use DERP relays to forward traffic from one node to another. DERP relays are normally used as a side channel, to help initially establish a direct connection, but in some cases such as with more complex firewall configurations, are used to relay all traffic.
To determine which devices you are actively connected to and whether they connect directly or use a relay, run:
tailscale status
To determine if a specific connection from your device to another device is using a relay, run:
tailscale ping <hostname-or-ip>
Latency vs security
Your organization may have configured a firewall to protect their network from unsolicited, unnecessary, or malicious traffic. Although the workarounds below may help Tailscale to establish direct connectivity between nodes, these may also make it easier for other traffic to reach your network. Before implementing any of these changes, consider if your organization wants to make this trade-off between security and latency.
Specifically:
- By enabling NAT-PMP and UPnP, your network can allow in and forward all traffic.
- By opening a firewall port, your network will allow traffic on a certain port and meeting certain rules to leave your network. Restrict this traffic only to what is needed. Subscribe to this GitHub issue for updates on a Tailscale ruleset.
Firewall compatibility and workarounds
| Firewall | Expected behavior | Workaround |
|---|---|---|
| Barracuda | Connects via DERP | Increase Max UDP sessions, and open a firewall port |
| Check Point | Connects directly | n/a |
| Cisco | Connects via DERP | Open a firewall port |
| Cisco with Cisco Umbrella Endpoint Security | Connects via DERP | None |
| Fortinet | Connects via DERP | Randomize port |
| Fortinet with FortiGate deep packet inspection | Unable to connect to control plane | None |
| OPNsense | Connects via DERP | Enable NAT-PMP, or static NAT port mappings |
| pfSense | Connects via DERP | Enable NAT-PMP, or static NAT port mappings |
| Palo Alto Networks | Connects via DERP | Use Persistent Dynamic IP and Port |
| Sophos | Connects directly | n/a |
| UniFi Gateways | Connects via DERP | Allow peer-to-peer traffic |
For other firewalls, if your connections are using DERP relays by default, try opening a port to establish a direct connection.
If you experience an issue with a firewall not listed here, or need help configuring a particular firewall with Tailscale, contact support.
Barracuda
In networks with Barracuda firewalls, Tailscale nodes will have difficulties making direct connections, and often resort to DERP relays.
To help Tailscale make direct connections, modify the maximum number of UDP sessions that a Barracuda firewall allows, making it easier for multiple Tailscale clients to connect, without competing with each other for UDP ports. To modify this, increase the "Max UDP" parameter in your firewall configuration.
You can also consider opening a firewall port.
Check Point
In networks with Check Point firewalls, Tailscale nodes should be able to establish direct connections by default.
Cisco
In networks with Cisco firewalls, Tailscale nodes will have difficulties making direct connections, and often resort to DERP relays.
To help Tailscale make direct connections, consider opening a firewall port.
Cisco Umbrella Endpoint Security
If you are using Cisco Umbrella Endpoint Security, then the above will not work to establish direct connections, and your traffic will always resort to DERP relays.
Cisco Umbrella DNS Filtering
For DNS filtering via Cisco Umbrella (formerly OpenDNS), Umbrella/OpenDNS will override DNS settings set by Tailscale without additional configuration. To configure the two together:
- Configure Umbrella/OpenDNS to send
*.<your-tailnet-name>.ts.netqueries to100.100.100.100.100.100.100.100or Quad100 is a special Tailscale IP address in your Tailscale network (known as a tailnet) that provides essential local services including a DNS resolver. - Disable MagicDNS in the Tailscale admin console.
- Disable Override DNS servers in the Tailscale admin console and on end-user clients with an MDM system policy.
This configures clients to continue to use Umbrella for all DNS queries, while configuring Umbrella to use Tailscale's Quad100 DNS resolver for tailnet-specific queries.
Fortinet
In networks with Fortinet firewalls, Tailscale nodes will have difficulties making direct connections, and often resort to DERP relays. This issue might not be present at a smaller scale, with issues occurring once more than 5 individuals are using Tailscale behind the same firewall.
To allow direct connections, in the Access controls tab of the admin console, include an option in your tailnet policy file to randomizeClientPort. This makes devices use a random port for WireGuard rather than the default static port 41641.
{
// Tailnet policy file settings and other configurations
"randomizeClientPort": true
}
If you are using FortiGate application control rules with certain configurations, your firewall will intercept HTTPS connections to the Tailscale control plane, and nodes in your network will be unable to connect to Tailscale. If this happens, a certificate verification error similar to the one below will display in the Tailscale client UI and in the output of the Tailscale CLI tailscale status command:
fetch control key: Get "https://controlplane.tailscale.com/key?v=123": x509: "controlplane.tailscale.com" certificate is not trusted
To address the issue, go to the FortiOS admin panel from a browser, select Security Profiles, then Application Control. Disable or reduce the scope of any security profiles that perform SSL inspection. In particular, verify that you are not using any default rules that block traffic belonging to the Proxy category or match against the Tailscale application defined in FortiGuard. This is currently the only known workaround.
OPNsense and pfSense
In networks with OPNsense and pfSense firewalls, Tailscale devices will have difficulties making direct connections and often resort to using DERP relay servers.
However, there are options to allow direct connections, such as NAT Port Mapping Protocol (NAT-PMP), static NAT port mapping, and Universal Plug and Play (UPnP). For more details, refer to the instructions for pfSense and OPNsense.
Tailscale can also be run directly on these routers using a plugin for pfSense and the FreeBSD Tailscale package for OPNsense.
Palo Alto Networks
Using Persistent Dynamic IP and Port in the NAT Policy translation type allows Tailscale to establish direct WireGuard connections through the firewall.
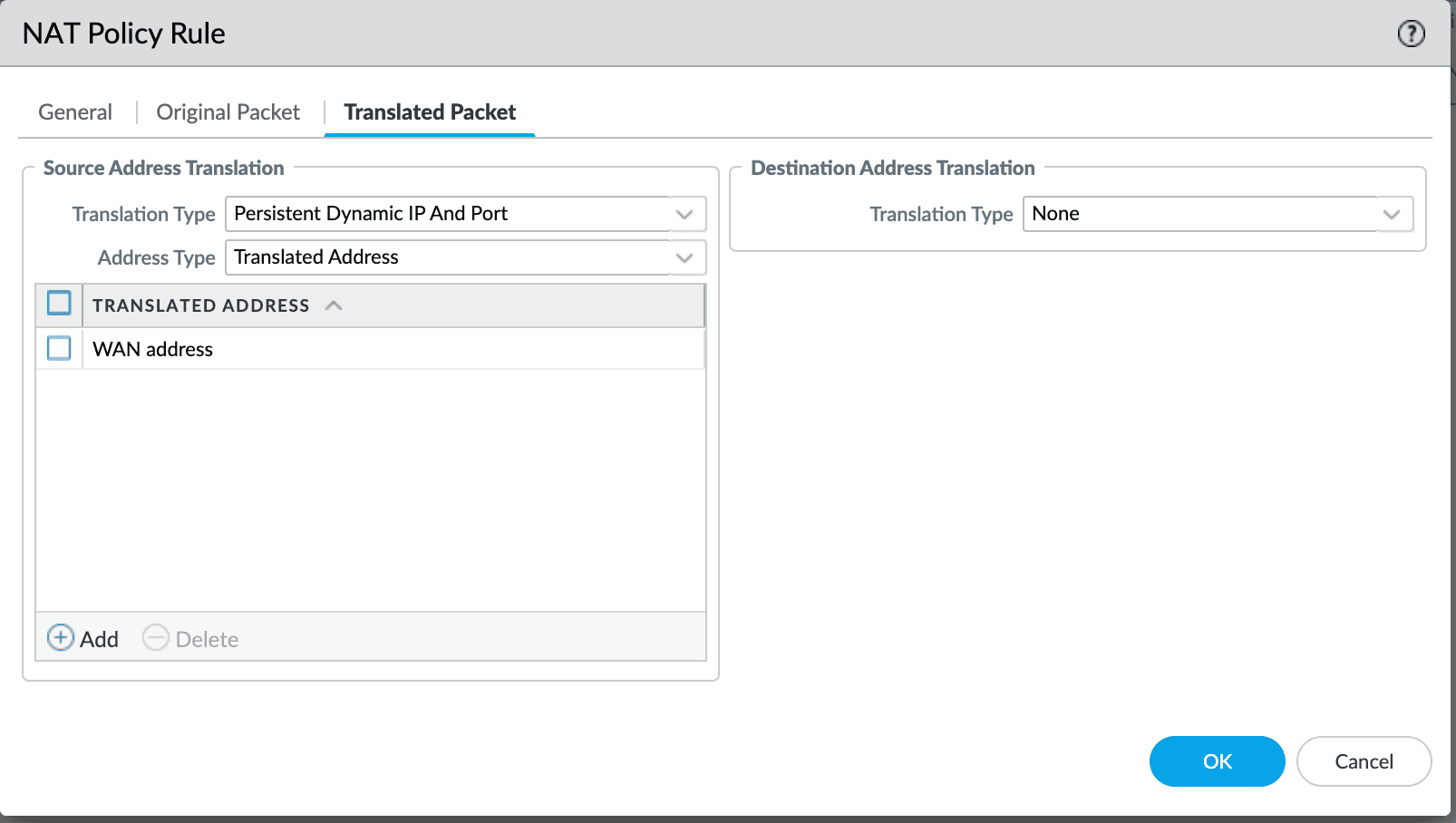
Persistent Dynamic IP support was added in PAN-OS 11.1.1. There is a separate topic for Palo Alto Networks firewalls covering more detail and several additional options.
Sophos
In networks with Sophos security gateways, the default firewall settings work well for Tailscale connectivity. A random port is chosen for the very first mapping, then that same port is used for all subsequent flows using the same source port. This allows Tailscale at the other end to know what port it should use for sending traffic.
To confirm this, use the Tailscale CLI command tailscale netcheck to ensure that MappingVariesByDestIP: false is the relevant point.
UniFi Gateways
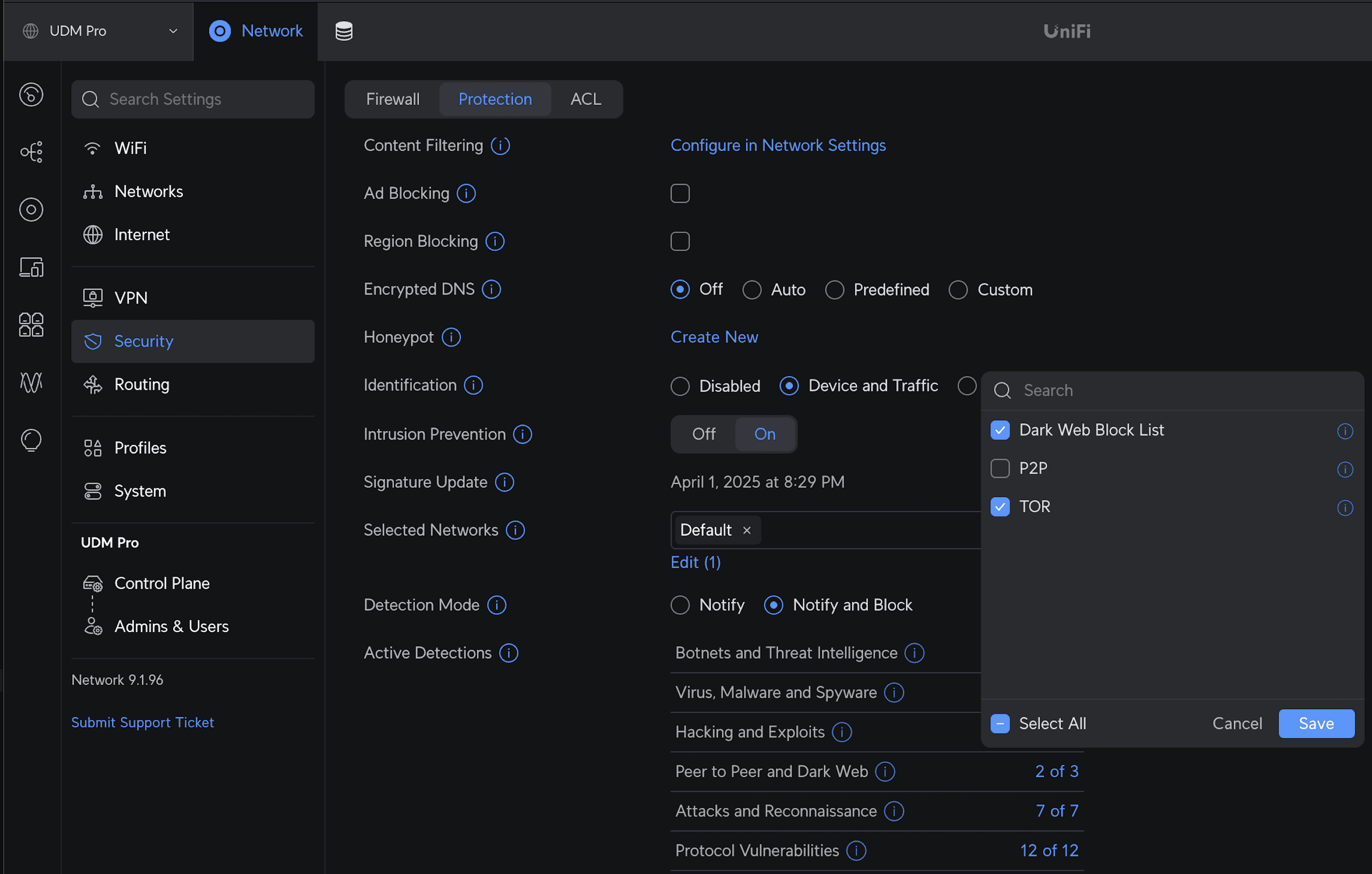
If you have a UniFi security gateway with threat detection enabled, make sure to allow peer-to-peer traffic for the nodes in your tailnet.
In UniFi Network version 9.0.107 and earlier, navigate to Settings, Firewall & Security, Edit threat categories, and uncheck P2P.
In UniFi Network version 9.0.108 and later, navigate to Network, Security, Protection, Peer to Peer and Dark Web, and uncheck P2P.
Only allow traffic over Tailscale
You can also use a firewall to restrict traffic in your network to require the use of Tailscale. For example, see instructions on using UFW to lock down an Ubuntu server.
