pfSense settings to enable direct connections
Last validated:
pfSense is an open source router and firewall platform built using FreeBSD. Tailscale clients behind a pfSense firewall can benefit from a settings change.
Tailscale can also be run directly on these routers, by using a plugin for pfSense.
Direct Connections for LAN Clients
As a router/firewall, pfSense may also be providing internet connectivity for LAN devices which themselves have a Tailscale client installed. The NAT implementation in pfSense is an Endpoint-Dependent Mapping, or "hard" NAT, which means that LAN devices have difficulty making direct connections and often resort to DERP Relays.
There are a few options in which pfSense can enable devices on the LAN to make direct connections to remote Tailscale nodes. Static NAT port mapping and NAT-PMP.
Static NAT port mapping
As of pfSense+ 25.11 and expected in the upcoming pfSense Community Edition 2.9.0, pfSense includes partial experimental support for "Port Restricted Cone" endpoint-independent outbound NAT (EIM-NAT).
These "Port Restricted Cone" NAT mappings can replace the randomizeClientPort suggestion for earlier versions.
By default, pfSense software rewrites the source port on all outgoing connections to enhance security and prevent direct exposure of internal port numbers.
Static port mapping in pfSense involves creating a fixed association between a specific external port number and an internal IP address and port, allowing incoming traffic to be directed to the correct destination within the local network.
Locate the Firewall > NAT, Outbound tab. Select Hybrid Outbound NAT rule generation. Select Save. Select ↑ Add to create a new NAT rule to the top of the list.
Configure the rule as shown below: IPv4+IPv6, for Protocol UDP, source address Any. Check Static Port in the Translation section of the page.
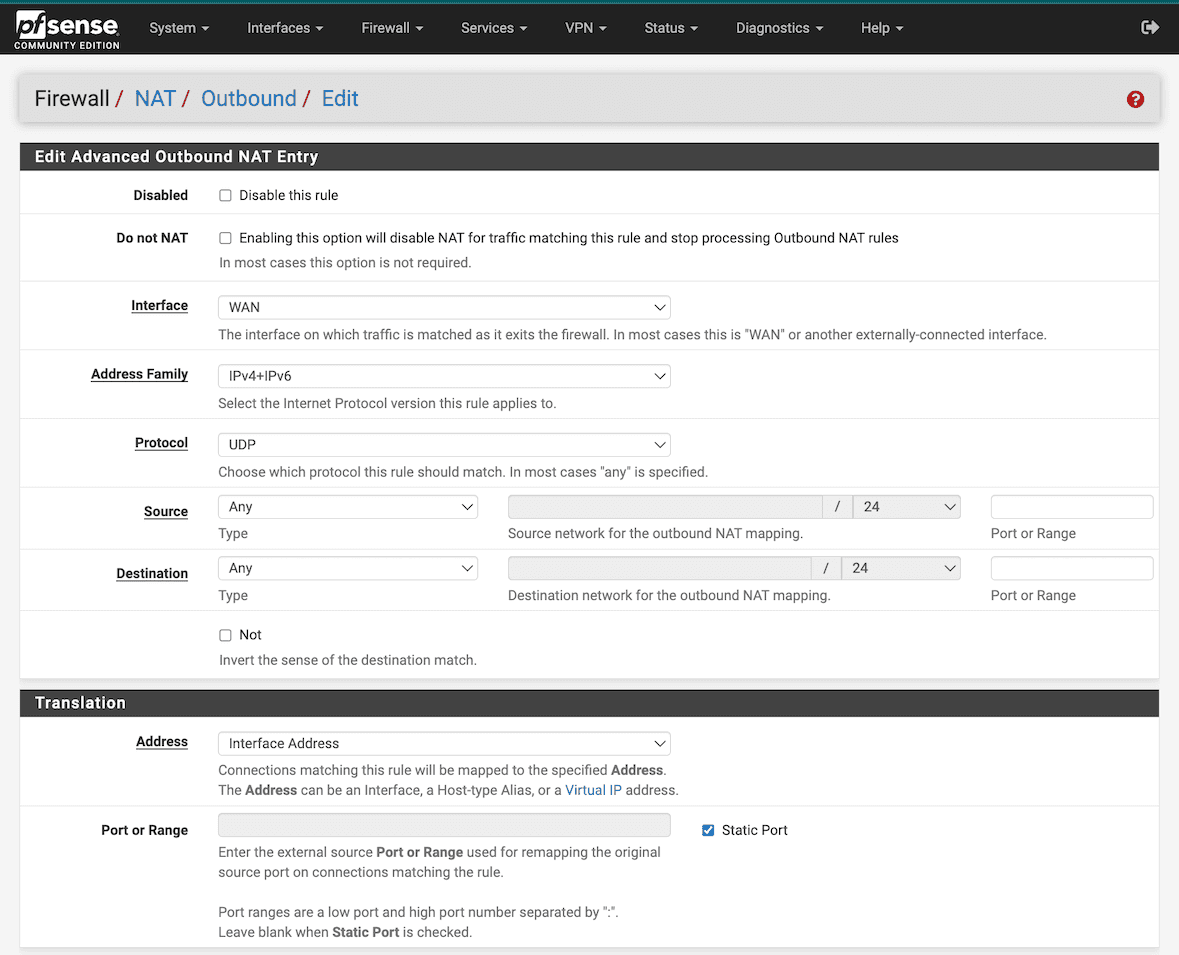
Select Save. Select Apply Changes.
In your ACLs, set randomizeClientPort.
{
// Other configurations
"randomizeClientPort": true
}
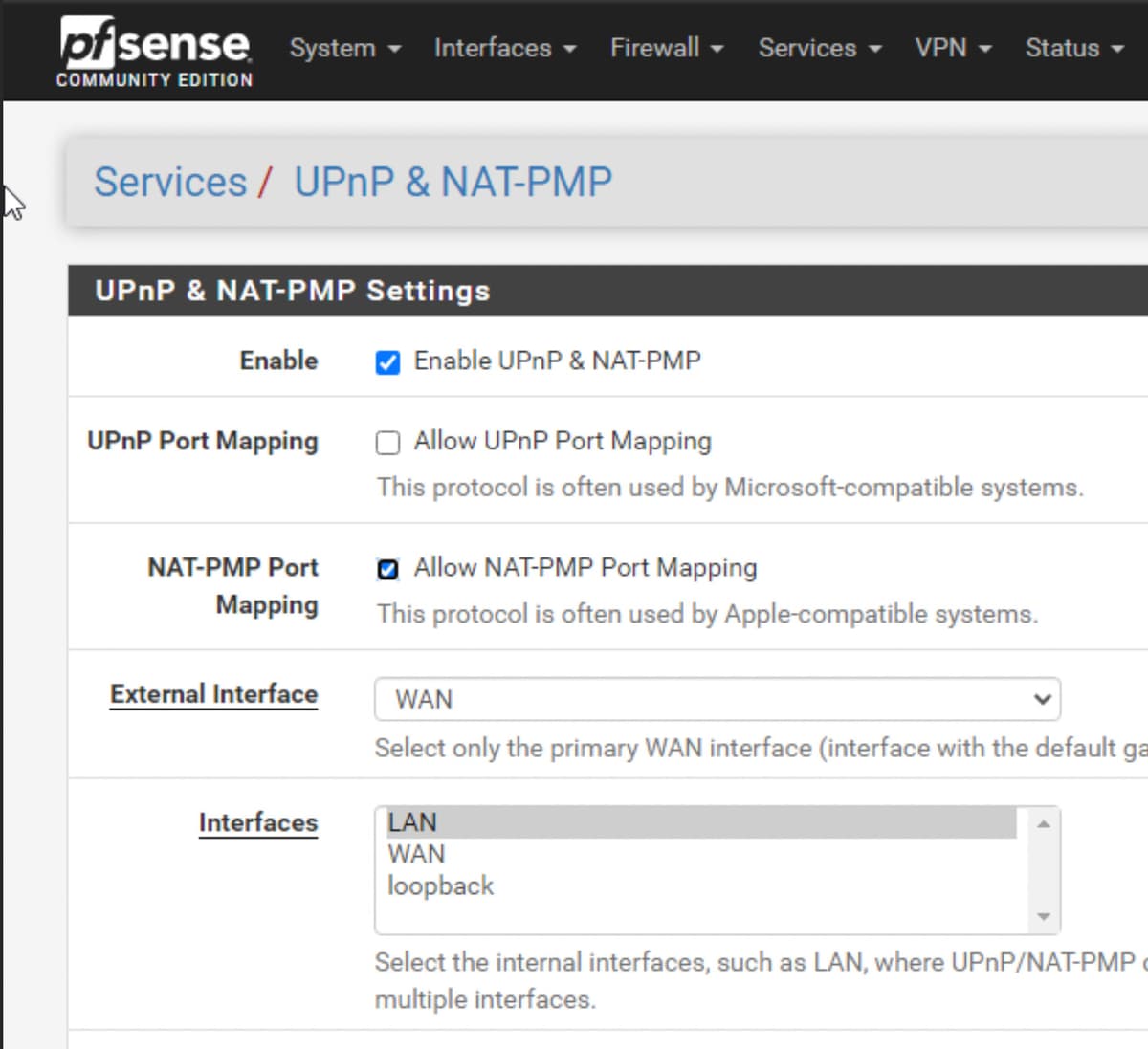
NAT-PMP
NAT-PMP is a protocol by which LAN clients can ask the firewall to temporarily create port mappings.
Enable the UPnP service and Allow NAT-PMP Port Mapping in Services > UPnP & NAT-PMP. Only NAT-PMP is needed for Tailscale's use, but enabling UPnP can be helpful for other applications like gaming consoles.